
이전 포스팅에서는 숫자형과 불리언 타입의 변수에 null을 대입할 수 있는 Nullable 타입을 소개했습니다.
이번 포스팅에서는 null과 관련된 연산자들을 정리합니다.
?? 연산자
피연산자가 null이 아닌 경우 왼쪽 피연산자의 값을 반환합니다.
피연산자가 null일 경우에는 오른쪽 피연산자의 값을 반환합니다.
a ?? b;a가 null이면, b가 반환됩니다.
a가 null이 아니면 a가 반환됩니다.
?? 연산자 사용 방법
int? a = null;
// a가 null이므로 오른쪽 피연산자(29)가 반환됩니다.
int b = a ?? 29;
Console.WriteLine(b);실행 결과

??= 연산자
왼쪽 피연산자가 null일 경우 오른쪽 피연산자의 값을 왼쪽 피연산자에 대입합니다.
int? a = null;
// 변수 a가 null일 경우 29를 변수 a에 대입합니다.
a ??= 29;?. 연산자
객체가 null이면 null을 반환하고 그렇지 않은 경우에는 . 뒤에 지정된 멤버의 값을 반환합니다.
객체를 null로 초기화 후 ?. 연산자를 사용한 코드입니다.
class Test
{
public int testCol;
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test test = null;
int? a;
// test가 null이면, null을 반환하며 그렇지 않으면, . 뒤에 있는 멤버(testCol)를 반환
a = test?.testCol;
// test가 null이므로 null이 반환되었음
Console.WriteLine(a == null);
}
}실행 결과

객체가 null이 아닌 경우입니다.
class Test
{
public int testCol;
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test test = new Test();
test.testCol = 29;
int? a;
// test가 null이면, null을 반환하며 그렇지 않으면, . 뒤에 있는 멤버(testCol)를 반환
a = test?.testCol;
// test가 null이 아니므로 멤버(testCol)가 반환되었음
Console.WriteLine(a == null);
Console.WriteLine(a);
}
}실행 결과

?[] 연산자
배열이 null이면 null을 반환하고 그렇지 않은 경우에는 [] 에 지정된 index의 값을 반환합니다.
ArrayList listA = null;
Console.WriteLine("listA[0] : {0}", listA?[0]);
ArrayList listB = new ArrayList();
listB?.Add("100");
Console.WriteLine("listB[0] : {0}", listB?[0]); 실행 결과

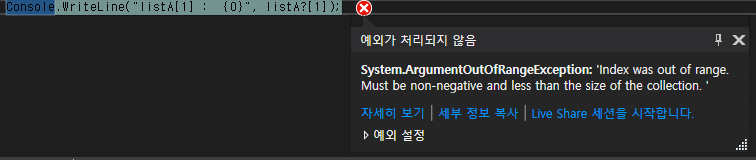
배열이 null은 아니지만, index가 크기를 벗어난 경우 IndexOutOfRangeException을 throw 합니다.
ArrayList listA = new ArrayList();
listA?.Add("100");
Console.WriteLine("listA[0] : {0}", listA?[0]);
Console.WriteLine("listA[1] : {0}", listA?[1]); 실행 결과
반응형
'C#' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C#]Call By Value, Call By Reference (0) | 2021.05.16 |
|---|---|
| [C#]값 형식(Value Types)과 참조 형식(Reference Types) (3) | 2021.05.15 |
| [C#]Nullable 타입 (3) | 2021.05.13 |
| [C#]자동 구현 프로퍼티(Auto Property) (0) | 2021.05.08 |
| [C#]프로퍼티(Property) - get, set 사용 (0) | 2021.05.08 |

댓글