기본 메서드(Default Method)
Java 8에 도입된 기본 메서드는 default 키워드를 사용하여 인터페이스(interface)에서 메서드를 구현하는 것입니다.
기본 메서드 도입 이전에는 인터페이스에 추상 메서드만 작성할 수 있었습니다. 추상 메서드는 메서드 본문이 없는 메서드입니다.
다음 예제는 인터페이스 내부에 메서드 본문이 없는 추상 메서드가 존재하므로 정상적으로 컴파일됩니다.
public interface InterfaceTest {
void printValue(String val);
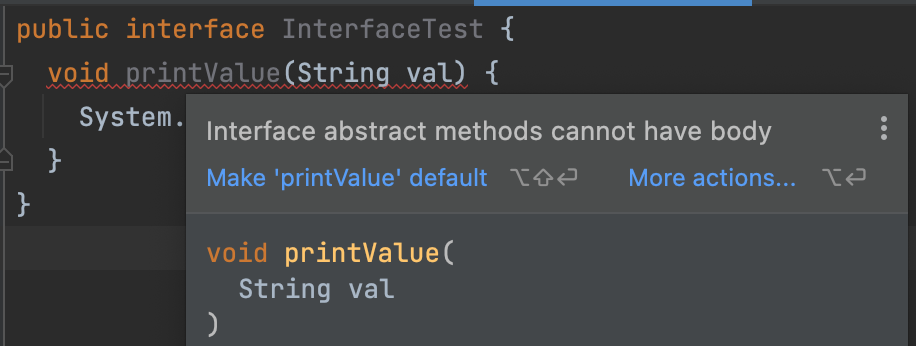
}하지만, 다음 예제는 추상 메서드에 메서드 본문이 존재하므로 컴파일 에러가 발생합니다.
public interface InterfaceTest {
void printValue(String val) {
System.out.println("val");
};
}실행 결과
Java 8 이전에는 인터페이스 내부의 추상 메서드를 재정의하기 위해 인터페이스를 상속받는 클래스에서 추상 메서드를 재정의(Overriding)해야만 했습니다. 하지만, Java 8부터 도입된 default 키워드를 사용하면 인터페이스에서 메서드 본문을 구현할 수 있습니다.
다음 예제는 default 키워드를 사용하여 인터페이스에서 기본 메서드를 정의하였으며, 객체를 생성하기 위해 인터페이스를 상속받는 클래스를 선언합니다.
public interface InterfaceTest {
default void printValue(String val) {
System.out.println(val);
}
}
public class ClassTest implements InterfaceTest{
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ClassTest obj = new ClassTest();
obj.printValue("Hi!!!");
}
}실행 결과
Hi!!!그리고 인터페이스에 정의된 기본 메서드는 구현 클래스에서 재정의할 수 있습니다. 다음 예제는 재정의된 메서드가 호출됩니다.
public interface InterfaceTest {
default void printValue(String val) {
System.out.println(val);
}
}
public class ClassTest implements InterfaceTest{
public void printValue(String val) {
System.out.println("Override");
System.out.println(val);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ClassTest obj = new ClassTest();
obj.printValue("Hi!!!");
}
}실행 결과
Override
Hi!!!기본 메서드 필요성 1. 단순화
여러 클래스에서 한 개의 인터페이스를 구현해야 하는 경우 모든 클래스에서 메서드를 구현해야 합니다. 공통적으로 사용되는 메서드는 인터페이스에서 기본 메서드로 정의하면 더 이상 클래스에서 추상 메서드를 구현하지 않아도 됩니다. 불필요한 작업은 줄이고 개발 속도는 높아지므로 작업이 단순화됩니다.
기본 메서드 필요성 2. 람다식
Java 8 이전에는 컬렉션 객체를 순회해야 하는 경우 반복자(Iterator) 객체를 생성하고 hasNext() 메서드를 사용했습니다. 다음 예제는 컬렉션 객체를 순회하는 가장 일반적인 방법입니다.
ArrayList aList = new ArrayList<String>();
aList.add("One");
aList.add("Two");
aList.add("Three");
// iterator() 메서드를 호출하여 Iterator 객체를 가져옵니다.
Iterator iterator = aList.iterator();
// hasNext() 메서드를 사용하여 컬렉션 객체를 순회합니다.
while( iterator.hasNext() ){
// next() 메서드를 사용하여 컬렉션 객체의 현재 요소를 가져옵니다.
System.out.println( iterator.next() );
}이제 위 예제처럼 반복자 객체를 생성하지 않아도 됩니다. Java 8부터 Iterable 인터페이스에 forEach() 기본 메서드가 추가되었기 때문입니다.
Iterable 인터페이스의 forEach() 메서드를 사용하여 위 소스코드를 간결하게 만들 수 있습니다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList aList = new ArrayList<String>();
aList.add("One");
aList.add("Two");
aList.add("Three");
aList.forEach((item) -> System.out.println(item));
}
}실행 결과
One
Two
Three다중 상속
클래스에서 여러 개의 인터페이스를 구현할 수 있으므로 다중 상속에 대해 의문점이 발생할 수 있습니다. 각각의 인터페이스에는 동일한 이름, 매개변수, 반환 타입을 가지는 기본 메서드가 존재하는 경우 클래스에서 컴파일 에러가 발생합니다.
public interface interface001 {
default void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("interface001의 defaultMethod() 메서드");
}
}
public interface interface002 {
default void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("interface002의 defaultMethod() 메서드");
}
}
public class TestClass implements
interface001, interface002 {
}실행 결과
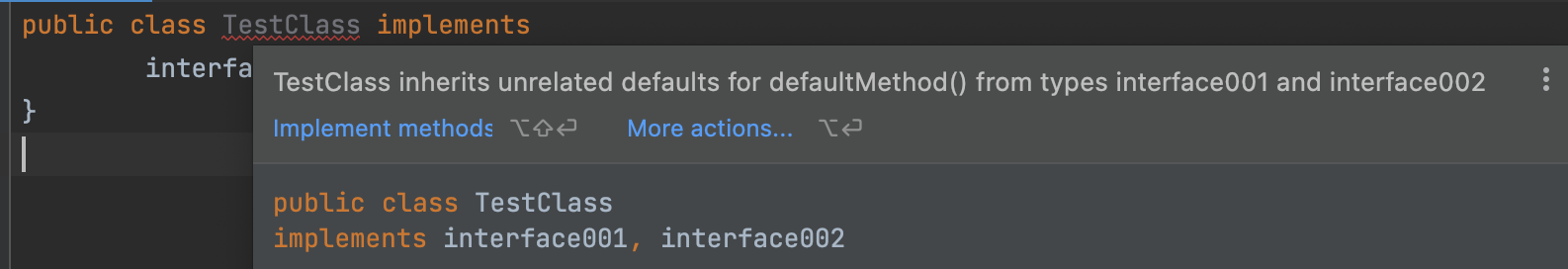
죽음의 다이아몬드라고 불리는 다중 인터페이스 상속으로 인해 컴파일 에러가 발생합니다.
TestClass 클래스는 어떤 인터페이스의 defaultMethod() 메서드를 호출해야 하는지 모르므로 충돌이 발생합니다.
위 문제를 해결하려면, 클래스에서 충돌이 발생한 메서드를 구현합니다.
public interface interface001 {
default void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("interface001의 defaultMethod() 메서드");
}
}
public interface interface002 {
default void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("interface002의 defaultMethod() 메서드");
}
}
public class TestClass implements
interface001, interface002 {
public void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("TestClass 클래스의 defaultMethod() 메서드");
}
}또 다른 방법으로 super 키워드와 Override 어노테이션을 사용하여 기본 메서드를 재정의할 수 있습니다.
public interface interface001 {
default void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("interface001의 defaultMethod() 메서드");
}
}
public interface interface002 {
default void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("interface002의 defaultMethod() 메서드");
}
}
public class TestClass implements
interface001, interface002 {
@Override
public void defaultMethod() {
interface001.super.defaultMethod();
interface002.super.defaultMethod();
}
}정리
- 기본 메서드는 default 키워드를 사용하여 인터페이스에서 메서드를 구현할 수 있습니다.
- 공통적으로 사용되는 메서드는 인터페이스에서 기본 메서드로 구현할 수 있습니다.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java]익명 클래스(Anonymous Class) (0) | 2022.06.21 |
|---|---|
| [Java]중첩 클래스 및 내부 클래스(Nested Class and Inner Class) (0) | 2022.06.21 |
| [Java]메서드 참조(Method reference) (0) | 2022.05.11 |
| [Java]람다식, 람다표현식(Lambda expression) (0) | 2022.05.10 |
| [Java]리플렉션(Reflection) (0) | 2022.05.08 |

댓글